Ethernet vs. Wi-Fi: What is the Difference?
Although you might think of WiFi and the internet as interchangeable terms, they provide different functions. WiFi provides a wireless connection to the internet for your devices. However, you can also access the internet at your office using an Ethernet cable, which offers a wired connection.
Many routers allow you to connect both wirelessly or via a wired connection and ultimately, the best choice depends on your business’ internet needs.
In this article, we will look into how both these approaches work and uncover some key comparisons to help you choose the best option for your internet connectivity.
What is Ethernet?
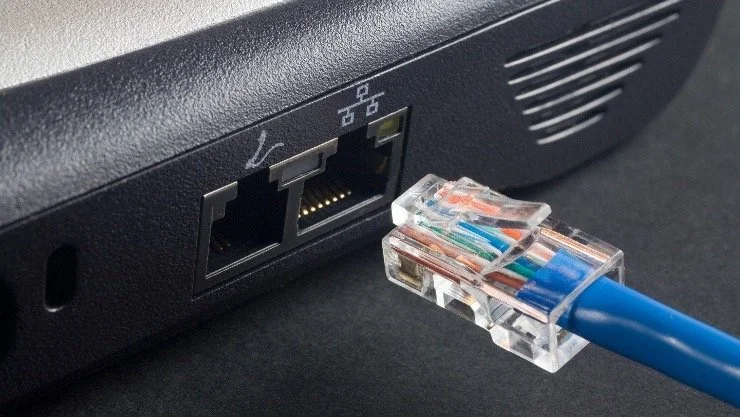
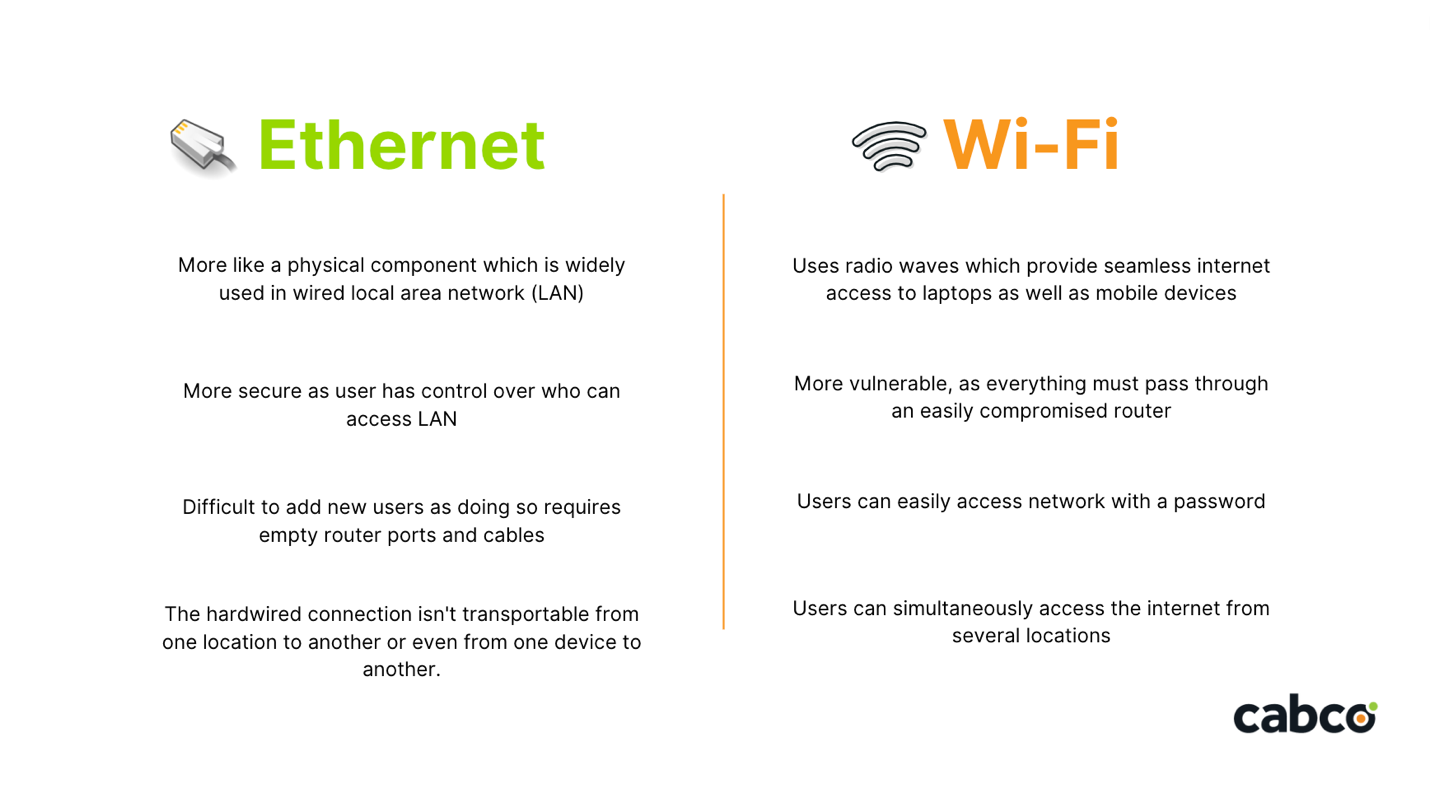
Ethernet is the most common type of local area network (LAN) technology that connects different devices in a network. It allows your devices to communicate via a protocol, which is a set of rules or common network language.
The origin of Ethernet was the idea of connecting several computers together in a network via coaxial cables; since that time, it has evolved into a much more sophisticated system that uses specialized Ethernet cables that run from a router, modem, or network switch to your computer, giving your device access to the LAN— and ultimately, the wider internet.
What is an Ethernet Cable?
An Ethernet cable, sometimes referred to as a network cable, is an encased set of wires that allows data to travel – helping carry internet signals, sending and receiving data packet requests and routing them to the proper computers on the network.
While Ethernet might seem slightly outdated in the age of wireless connection, it remains highly useful for particular, intensive tasks, such as video streaming and virtual communication as it provides more reliable speeds than Wi-Fi without the involvement of any outside interference such as walls or other objects blocking your signal. (We will look closer at this in the comparison section of this article).
What is WiFi?
Wi-Fi is a network technology that enables devices to connect to the internet wirelessly. Unlike an ethernet connection, this technology uses radio waves to transmit information between your device and a router via frequencies.
Wireless LANs have exponentially evolved from high-priced network solutions to mainstream innovation in just a few years. The elimination of the networking port from the equation and separating the device connection from the direct physical position at the end of the cord has certainly made wireless LANs simple and functional. The best thing about wireless service is a mobility-without cable; no cabling means easy movement and expansion.
To learn more about the optimization of Wi-Fi networks, check out our ‘A Deeper Dive on Wi-Fi’ blog post.
What are the Key Differences Between Ethernet and WiFi?
Here are the key differences between a wired and wireless connection and how it can impact your internet speed.
1. Speed
An Ethernet connection is almost always faster than Wi-Fi because it uses a cable to transfer data nearly instantaneously, whereas a wireless network relies on the comparatively slow and diffuse transfer of data over radio waves.
It’s important to note that speeds will not exceed the amount offered on your plan, regardless of whether you’re using WIFI or an ethernet connection. For example, if you’re paying for 150 Mbps, that’s the maximum speed you’ll get on an ethernet cable or WIFI connection. The difference is that an ethernet connection isn’t interrupted by outside interferences and can consistently offer the speeds available on your router.
2. Security
Ethernet connections tend to be more secure as your data can only be accessed by plugging a device into your network with an Ethernet cable. Additionally, you can control who has access to the LAN.
On the other hand, data on a Wi-Fi network is more vulnerable, as everything must pass through an easily compromised router. Numerous kinds of attacks can be carried out remotely, such as reauthenticating a device, or cracking the encryption key to get into the network. An example of a common threat is one which uses fake access points, where the victim connects to an open network which was created by the attacker, who then spies on the user’s traffic and steals their data.
These attacks are impossible to carry out remotely through an Ethernet network, as an attacker would need physical access to do so. This is why, cable connections ensure greater security than wireless, or, in other words, they offer a lower risk of incidents if you do not have an IT team to set up intensive security measures on your network.
3. Accessibility
Wi-Fi gets the edge when it comes to accessibility. When you enter the password for the network, you're connected as long as you're in range. This means it's perfect for portable devices such as smartphones, tablets, and laptops. Even inexperienced users can quickly find a Wi-Fi network to join and enter a password.
When it comes to Ethernet networks, it can be difficult to add new users as doing so requires empty router ports and cables, and many devices such as tablets and mobile phones don't have built-in Ethernet ports.
4. Mobility
It goes without saying that the greatest strength associated with a WiFi network is its mobility as users can simultaneously access the internet from several locations. Wireless Internet means no cables and no ports - users are able to easily switch between rooms and cubicles without interrupting their workflow.
On the contrary, the hardwired, physical connection of Ethernet isn't easily transportable from one location to another or even from one device to another.
5. Cost
There isn’t a clear winner between Ethernet and Wi-Fi when it comes to cost. If your internet service provider (ISP) provides a modem and router, chances are you’re renting the equipment or paying a separate fee for wireless access. Over time, that can add up, so you’re better off purchasing a modem and router.
However, opting for a managed Wi-Fi solution can significantly decrease your cost of ownership because having a third-party Wi-fi provider allows your business to cut any costs associated with the need for an on-site IT department.
Ethernet can be costly too. The amount of cable you need to reach every area you can easily access over Wi-Fi—at a low-quality connection and likely the reason why you’re running Ethernet in the first place—could get expensive, depending on the length, quality, and generation of cable.
The bottom line here is that Wi-Fi may be cheaper if your wireless devices are in close range and you have a decent speed for what you need. The cost ultimately depends on your environment and what you need for a good connection.
Our Verdict – A Combination of Both for Best Results
As Atlantic Canada’s oldest independent communications integrator, we have customers who have been trusting us for 40 years, managing all their telecommunication needs to keep them connected.
We’ve learnt that a combination of Ethernet and Wi-Fi is ideal. There is no reason why your office cannot have both internet connectivity approaches.
From a broad perspective, you should keep sensitive data and more intensive processes to wired connections, and use wireless connections for sharing data and completing everyday work tasks that don’t require stringent security requirements.
Wi-Fi is the best way to take advantage of a device's portability. Use Wi-Fi with your smartphones and other portable devices, such as laptops and tablets. You won't notice a speed difference and the convenience of Wi-Fi trumps all.
Keep your router up to date at all times and to use a secure password, so there's no risk of anyone else accessing your office network. That way, you can enjoy the best of both worlds.
Still have questions regarding Ethernet and Wi-Fi solutions or just simply want to learn more about the two approaches? Reach out to us and we’ll be more than happy to discuss a suitable internet connectivity solution for your needs.
Ahona Saha
Marketing Assistant
Cabco